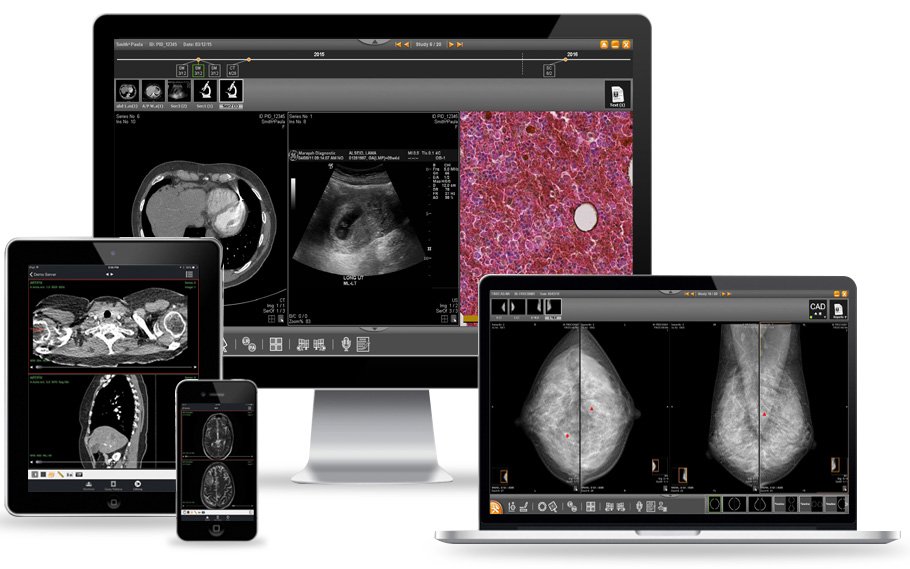
Picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) are essential medical imaging technology that optimizes workflows and provides secure storage and access to images like X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and more. This comprehensive guide covers PACS capabilities, components, benefits, top vendors, implementation considerations, and the future landscape.
What is PACS?
PACS is a medical imaging technology that captures images from modalities like X-ray machines, stores them in a secure, centralized archive, distributes them to appropriate systems, and displays them for clinicians.
Key capabilities of PACS include:
- Acquiring images from imaging equipment (modalities)
- Securely transmitting images over networks
- Long-term storage in centralized archives
- Quick access to images for diagnosis and review
- Advanced visualization of multi-dimensional imaging
- Integration with electronic medical records (EMRs)
- Web-based distribution of images across enterprises
PACS replaces older film-based workflows and provides a modern digital imaging infrastructure for healthcare systems.
Components of a PACS System
A PACS system consists of integrated hardware and software:
Image modalities
- X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, nuclear medicine, etc.
Secure networks
- High-speed LANs, WANs, VPNs, firewalls
Workstations
- Diagnostic, clinical review, 3D post-processing
Archives
- Short-term, long-term, disaster recovery
Software
- DICOM networking, viewers, workflow managers
EMR integration
- HL7 interfaces with electronic medical records
Key Benefits of PACS
PACS systems transform imaging workflows and offer major benefits:
- Improved clinician productivity – Instant access to images from any location
- Enhanced diagnostics – Specialized 2D, 3D, and 4D visualization
- Lower costs – Eliminates expenses of film and transport
- Better patient care – Speeds image access for urgent cases
- Superior image management – Consolidated, redundant archives
- Reduced errors – Replaces handwritten notes on films
- Space savings – No storage rooms for mountains of film
Top PACS Vendors
Major PACS vendors include:
- GE Healthcare – Centricity PACS
- Philips – IntelliSpace PACS
- Sectra – Sectra PACS
- FujiFilm – Synapse PACS
- Carestream – Vue PACS
- Novarad – NovaPACS
- DR Systems – IMAGEnet PACS
- Candelis – Candelis PACS
- Infinitt – Infinitt PACS
Vendors compete on breadth of capability, performance, scalability, specialty workflows, analytics, and enterprise integration.
PACS Architecture and Components
Modern PACS leverage a distributed architecture:
Image acquisition
- X-ray, CT, ultrasound, etc., convert analog data to DICOM digital images
Modality workstations
- Enable technologists to ensure image quality
Secure DICOM networks
- Transmit imaging studies over hospital LANs and WANs
Short-term archives
- Cache recent images for rapid access
Long-term archives
- Provide high-capacity redundant storage
Databases
- Store information like patient demographics and study metadata
Diagnostic workstations
- High-resolution displays for radiologists to interpret images
Web servers
- Allow browser-based image access on desktops or mobile devices
Cloud storage
- Leverage scalable storage infrastructure
PACS Clinical Workflows
PACS supports critical workflows:
Image Order
- The physician enters the imaging order into HIS/RIS.
Scheduling
- The patient scheduled an appointment
Registration
- Patient information is entered into the RIS.
Acquisition
- The technologist performs an exam, and images are captured.
Transmission
- Images sent to PACS archives
Diagnosis
- Radiologist interprets images on a diagnostic workstation.
Reporting
- Radiologist dictates findings into voice recognition
Results distribution
- Images and reports distributed to the healthcare team
Image and report storage
- Safely stored in PACS long-term
Implementing PACS Systems
Implementing PACS requires careful planning and execution:
- Define clinical, operational, and technical requirements
- Evaluate leading vendor solutions
- Validate DICOM conformance and IHE integration profiles
- Assess infrastructure needs like networks, archives, workstations
- Develop deployment strategy and timeline
- Create a test environment to validate the performance
- Integrate with HIS, RIS, EMRs, and modalities
- Migrate legacy imaging data to new PACS databases
- Optimize workflows, train users, tune as needed post-implementation
Ongoing management requires administering security, managing software updates, maintaining workstations, providing user support, and running backup processes.
The Future of PACS Technology
Key trends shaping PACS innovation:
- Move to cloud infrastructure for storage, networking, and disaster recovery
- Leveraging AI for workflow optimization, predictive analytics, and quantitative imaging
- Expanding enterprise imaging strategies beyond radiology into -omics disciplines
- Enhanced clinical collaboration via web and mobile image access
- Voice recognition, VR/AR, and advanced visualization techniques
- Patient engagement via portals to view and manage imaging records
PACS systems will continue advancing to meet growing demands for optimizing imaging workflows, enhancing diagnostics, and securely connecting medical imaging across the health ecosystem.